Checking for non-preferred file/folder path names (may take a long time depending on the number of files/folders) ...
This resource contains some files/folders that have non-preferred characters in their name. Show non-conforming files/folders.
This resource contains content types with files that need to be updated to match with metadata changes. Show content type files that need updating.
| Authors: |
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Owners: |
|
This resource does not have an owner who is an active HydroShare user. Contact CUAHSI (help@cuahsi.org) for information on this resource. |
| Type: | Resource | |
| Storage: | The size of this resource is 2.2 MB | |
| Created: | May 09, 2023 at 12:44 p.m. | |
| Last updated: | May 28, 2024 at 3:54 p.m. | |
| Citation: | See how to cite this resource | |
| Content types: | Single File Content Geographic Feature Content |
| Sharing Status: | Public |
|---|---|
| Views: | 1120 |
| Downloads: | 935 |
| +1 Votes: | 2 others +1 this |
| Comments: | No comments (yet) |
Abstract
This resource was first created for a live demo during an online I-GUIDE VCO meeting on May 9, 2023. It was then modified for another live demo during the 1st annual CIROH users and developers conference in Salt Lake City, May 16-18. Recently, it was used for the National Water Center Summer Institute 2023.
It contains codes and inputs for a precipitation analysis across the Logan River Watershed. In this analysis, we will obtain modeled precipitation from two products: AORC and PRISM, compare the basin's average daily precipitation, and save results back to HydroShare.
Subject Keywords
Coverage
Spatial
Content
readme.md
Comparing basin averaged AORC precipitation datasets over the Logan River Watershed
Content of this resource:
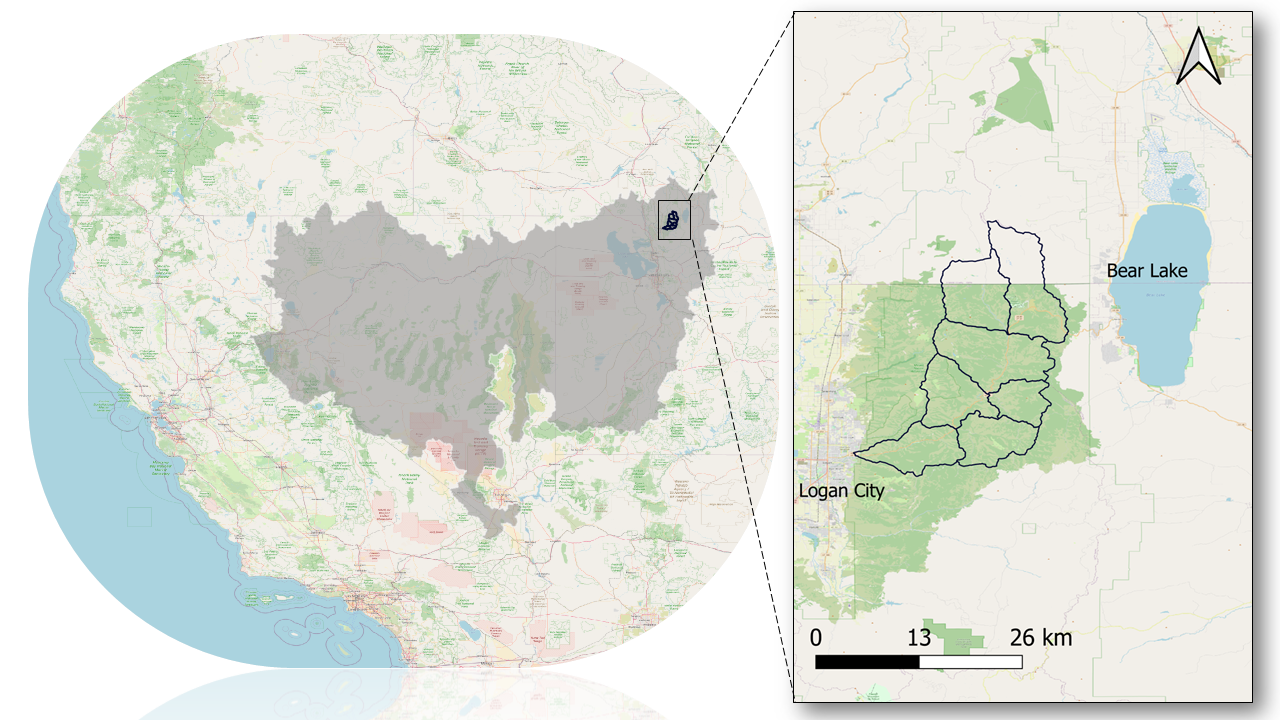
This example demonstrates how to collect and visualize the AORC (version 1.1) and PRISM precipitation data and calculate the basin averaged precipitation from both datasets over the Logan River Watershed in Utah (Figure below). This HydroShare resource contains the following items:
-
logan-watershed-huc12.shp: This is the shapefile of the Logan River Watershed that contains seven features (HUC 12 catchments). This file is a subset of the National Hydrography Dataset (NHD) and was retrieved from the USGS website.
-
Daily_PRISM_Precipitation_in_2010_for_LoganRiverWatershed.csv: This is the PRISM daily precipitation spatially averaged across the Logan River Watershed. This file was created using query-daily-prism-precipitation.ipynb.
-
query-daily-prism-precipitation.ipynb: This is a computational Jupyter Notebook in Python that downloads the PRISM precipitation data and clipped them for the Logan River Watershed.
-
query-aorc-and-compare-with-prism.ipynb: This is a computational Jupyter Notebook in Python that retrieves the AORC forcing data, clipped them for the Logan River Watershed, and compare these data with the PRISM precipitation (Daily_PRISM_Precipitation_in_2010_for_LoganRiverWatershed.csv).
-
readme.md: This is the readme file explaining the resource and its files.
-
case-study-logan-river-watershed.png: This is an image showing the geographical location of the study site. This image is referenced in this readme file.
Data used for this exercise:
Analysis of Record for Calibration (AORC)
The Analysis of Record for Calibration (AORC) is a gridded record of near-surface weather conditions covering the continental United States and Alaska and their hydrologically contributing areas. It is defined on a latitude/longitude spatial grid with a mesh length of ~800 m (30 arc seconds), and a temporal resolution of one hour. Elements include hourly total precipitation, temperature, specific humidity, terrain-level pressure, downward longwave and shortwave radiation, and west-east and south-north wind components. It spans the period from 1979 at Continental U.S. (CONUS) locations / 1981 in Alaska, to the near-present (at all locations). This suite of eight variables is sufficient to drive most land-surface and hydrologic models and is used to force the calibration run of the National Water Model (NWM).
Parameter-elevation Regressions on Independent Slopes Model (PRISM)
The PRISM Climate Data from Oregon State University is a gridded product covering the Conterminous United States. It combines climate observations from a wide range of monitoring networks with sophisticated modeling techniques to establish a local climate-elevation relationship for each grid cell. This relationship is then utilized to estimate various climate variables such as precipitation. This dataset spans from 1895 to the present and can be used to analyze short- and long-term climate patterns. The PRISM dataset is widely used across multiple disciplines, such as hydrology, climatology, agriculture, and environmental sciences and its popularity stems from its high spatial resolution, long-term record, reliable data quality, and ease of accessibility. It is worth noting that the PRISM dataset is available at two distinct spatial scales. The 4 km version is accessible to the public, while a more refined 800 m resolution dataset is available for a fee. For our purposes, we will be utilizing the publicly available 4 km resolution dataset.
Watershed Boundary Dataset (WBD):
The Watershed Boundary Dataset (WBD) is a seamless, national hydrologic unit dataset. Hydrologic units represent the area of the landscape that drains to a portion of the stream network. More specifically, a hydrologic unit defines the areal extent of surface water drainage to an outlet point on a dendritic stream network or to multiple outlet points where the stream network is not dendritic. WBD contains eight levels of progressive hydrologic units (HUC) identified by unique 2- to 16-digit codes. The case study region was selected from the HUC 12 watershed boundaries for the Great Basin from this HydroShare resource.
Case study:
The Logan River Watershed is a snowmelt-dominated watershed located in the Bear River mountain range east of Logan, Utah. Most precipitation falls in the form of snowfall during winter months and as rain during spring and summer time. Water flows southwest through mostly natural land cover.
How to run computational notebooks:
To access the CUAHSI JupyterHub, you have two options. First, you can right-click on any of the Jupyter Notebooks within this resource and choose the CUAHSI JupyterHub option. Alternatively, you can open the entire resource by clicking on the Open with button located at the top right corner of the landing page. Once you're in the resource, make sure to select the Python 3.8 server, and then follow the steps provided in the notebook.
Data Services
Related Resources
| The content of this resource can be executed by | https://jupyterhub.cuahsi.org/ |
| The content of this resource references | Horsburgh, J. S., S. S. Black (2021). HydroShare Python Client Library (hsclient) Usage Examples, HydroShare, http://www.hydroshare.org/resource/7561aa12fd824ebb8edbee05af19b910 |
Credits
Funding Agencies
This resource was created using funding from the following sources:
| Agency Name | Award Title | Award Number |
|---|---|---|
| National Science Foundation | HDR Institute: Geospatial Understanding through an Integrative Discovery Environment | 2118329 |
| National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration | CIROH: CUAHSI HydroShare Modernization | A22-0306-S004 |
Contributors
People or Organizations that contributed technically, materially, financially, or provided general support for the creation of the resource's content but are not considered authors.
| Name | Organization | Address | Phone | Author Identifiers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CUAHSI | Consortium of Universities for the Advancement of Hydrological Science | Massachusetts, US |
How to Cite
This resource is shared under the Creative Commons Attribution CC BY.
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Comments
There are currently no comments
New Comment